Anderson-Rubin Confidence Intervals based on feols IV regression objects
In this vignette, we demonstrate how to compute Anderson-Rubin confidence intervals for instrumental variables regression models estimated using the feols function from the fixest package. The Anderson-Rubin method provides robust inference in the presence of weak instruments.
We will use the built-in mtcars dataset for illustration. In this example, we will regress mpg (miles per gallon) on cyl (number of cylinders) using hp (horsepower) as an endogenous regressor and qsec (1/4 mile time) as an instrument.
First, we run a regression using feols.
Second, we compute the Anderson-Rubin confidence intervals for the coefficient of the endogenous regressor hp using the ar_ci function from the arci package.
Then, we visualize the results and extract the confidence intervals using the get_ar_ci function.
Finally, we use get_ar_ci to extract the computed confidence intervals in a tidy format.
library(fixest)
regression <- feols(mpg ~ cyl | hp ~ qsec, data = mtcars)
etable(regression)
#> regression
#> Dependent Var.: mpg
#>
#> Constant 39.65*** (3.115)
#> hp 0.0347 (0.0373)
#> cyl -3.983** (1.251)
#> _______________ ________________
#> S.E. type IID
#> Observations 32
#> R2 0.73733
#> Adj. R2 0.71921
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
arci_results <- ar_ci(regression, param = "hp", level = 0.95)
print(arci_results)
#> Anderson-Rubin95%Confidence Set for 'hp'
#>
#> The confidence set is the union of the following interval(s):
#> [-0.0247, 0.2193]
plot(arci_results)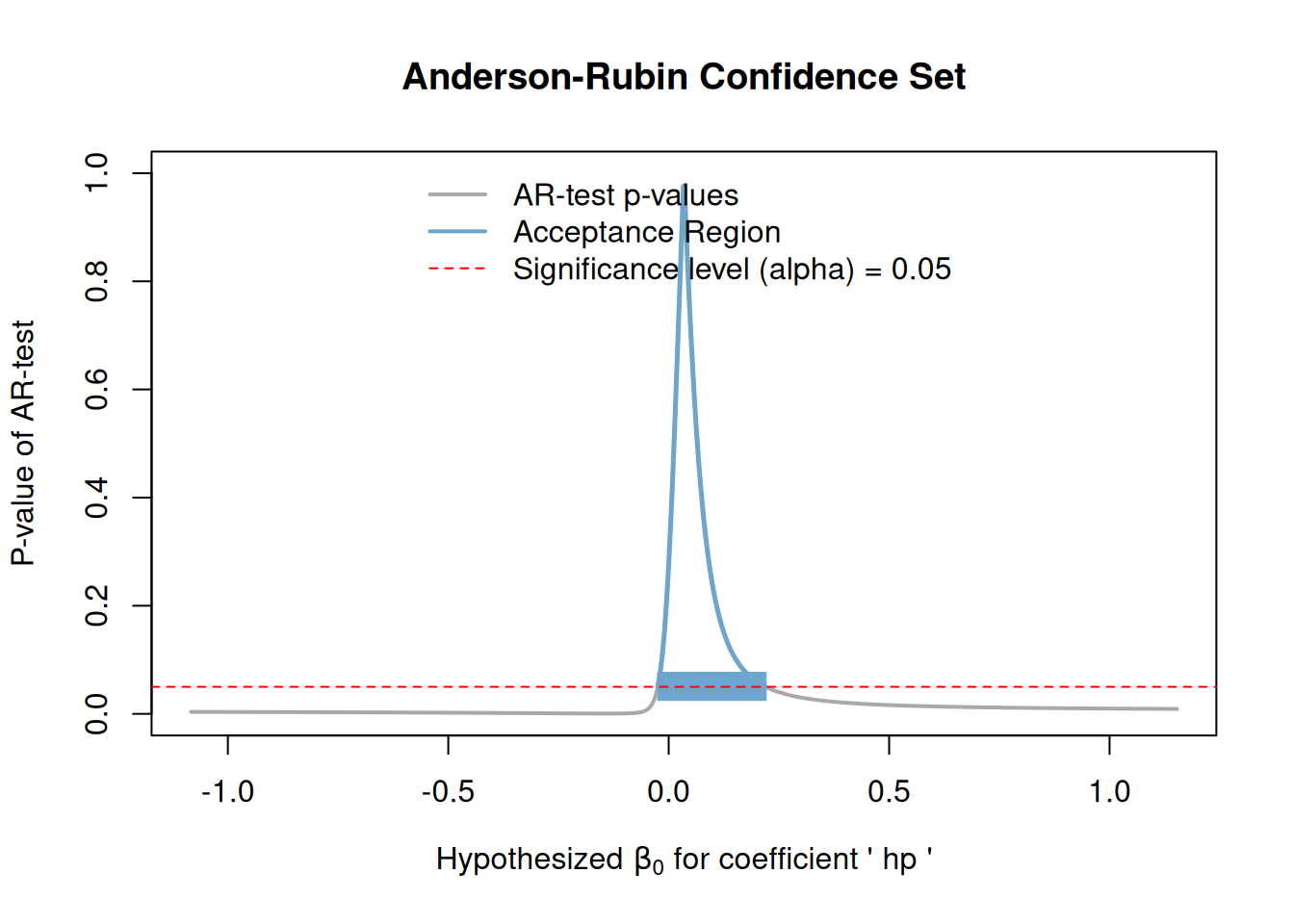
get_ar_ci(regression)
#> [1] "[-0.025, 0.219]"